 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站! 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!

截至目前,引用Bioss產品發表的文獻共36,822篇,總影響因子185,630.81分,發表在Nature, Science, Cell, Cancer Cell以及Immunity等頂刊的文獻共129篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復旦、華盛頓大學、麻省理工學院、東京大學以及紐約大學等上百所國際研究機構。
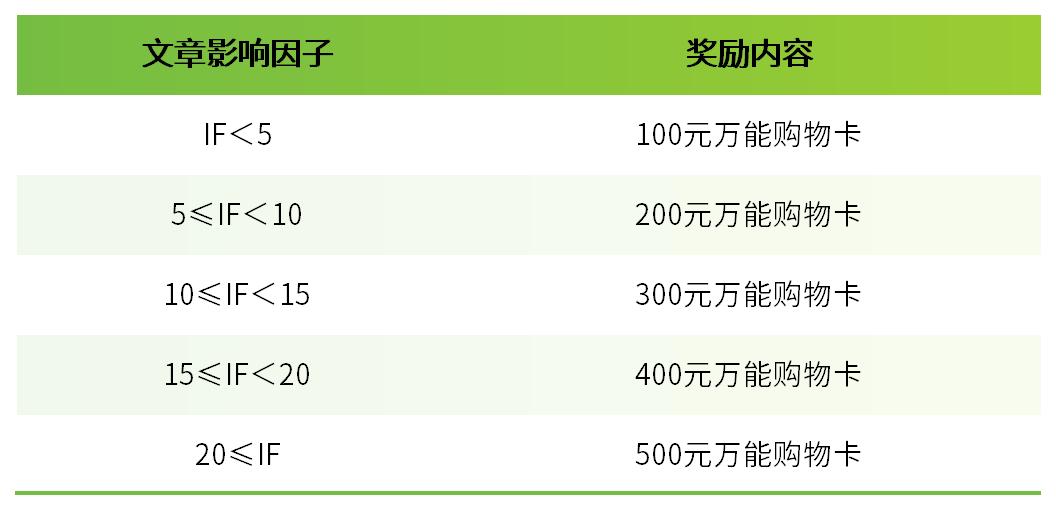
我們每月收集引用Bioss產品發表的文獻。若您在當月已發表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,請致電Bioss,我們將贈予現金鼓勵,金額標準請參考“發文章 領獎金"活動頁面。
本文主要分享9篇IF≥16的文獻,它們引用了Bioss產品,分別發表在Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy、European Heart Journal、Cancer Discovery、American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine、Advanced Functional Materials、ACS Nano期刊上,讓我們一起學習吧。
Signal Transduction and
Targeted Therapy [IF=52.7]
文獻引用產品:
bs-0296G-BF647 | Goat Anti-Mouse IgG H&L, BF647 conjugated | IF
C02-04002 | DAPI solution (Nuclear Labeling) | Other
作者單位:Army Medical University
摘要:Alpha hemolysin, a pore-forming toxin from Staphylococcus aureus, is a critical virulence factor for bacteria. Previous studies have demonstrated that the Hla mutant H35A (HlaH35A) serves as a potent carrier protein for subunit vaccines, yet its immunomodulatory mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Here, we demonstrate that the HlaH35A fusion enhances vaccine efficacy by targeting A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 10 (ADAM10) on dendritic cells (DCs), thereby activating the ADAM10-Notch signaling axis. Using the candidate antigen PA0833 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a model, we show that the HlaH35A-PA0833 fusion protein (HPF) significantly augments antigen uptake, DC maturation, and Notch-dependent transcriptional programs, particularly in conventional DCs (cDCs). The HlaH35A fusion drives the differentiation of Notch2-dependent cDC2s, which is marked by ESAM expression and IL-23 secretion. This process promotes Th17 and T follicular helper (Tfh) cell responses in draining lymph nodes, leading to elevated antigen-specific IgG1 titers and robust protection against acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Notably, ADAM10 or Notch inhibition abrogates these effects. Similarly, human monocyte-derived DCs exhibit enhanced maturation and Notch activation via the HlaH35A-ADAM10 interaction. Our findings reveal that HlaH35A is a novel carrier protein that shapes adaptive immunity by modulating cDC2 differentiation via ADAM10-Notch2 signaling, suggesting a promising strategy for Th17/Tfh-oriented vaccine design.
European Heart Journal [IF=35.6]

文獻引用產品:
bs-12028R | GPR105 Rabbit pAb | WB
作者單位:中國藥科大學
Background and Aims
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a disease related to high mortality and complications. Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation promotes thrombo-inflammatory responses, exacerbating VTE. P2Y14 receptor (P2Y14R), which is highly expressed on neutrophils mediates NET formation, but its role and mechanism in VTE are unclear. This study aims to explore the role and mechanism of P2Y14R in VTE and to investigate the feasibility of P2Y14R-targeting therapy for VTE.
Methods
Venous blood of VTE patients was collected to detect the expression of P2Y14R. Deep vein thrombosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation models were developed to detect thrombus and NET formation in wild-type and neutrophil P2Y14R deficiency mice. Transcriptomics, phosphorylated proteomics, and immunofluorescence were performed to investigate the mechanisms. A high-throughput Glide docking pipeline was performed to find potent P2Y14R antagonists from repurposing drug library.
Results
Neutrophil P2Y14R of VTE patients was significantly increased. Neutrophil-specific P2Y14R deficiency alleviated venous thrombosis and NET formation in mice. Mechanistically, neutrophil P2Y14R deletion promotes PKA-induced AKAP13 phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting RhoA activation and cytoskeleton rearrangement, resulting in reduced neutrophil-platelet aggregates and NET release. Interestingly, proglumide was identified as a potent P2Y14R antagonist with excellent P2Y14R antagonistic activity and binding affinity, of which the pharmacodynamic effect and mechanism on thrombosis and NET formation were verified.
Conclusions
Neutrophil P2Y14R deficiency regulates PKA/AKAP13/RhoA pathway to inhibit neutrophil-platelet aggregate, thereby reducing NET release and venous thrombosis. This indicates that P2Y14R may be a potential therapeutic target for the intervention of VTE using P2Y14R antagonists, including proglumide.
Cancer Discovery [IF=33.3]

文獻引用產品:
作者單位:休斯敦貝勒醫學院
摘要:Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype of breast cancer with few effective targeted therapies. Taxanes and other microtubule-targeting agents (MTA) are first-line chemotherapies for TNBC; however, the molecular mechanisms that underlie TNBC taxane sensitivity are largely unknown, preventing selection of taxane-responsive patients and development of more selective therapeutic strategies. In this study, we identified tumor-selective vulnerabilities in TNBC harboring inactivation of the tumor suppressor PTPN12 by integrating proteogenomic characterization and synthetic lethality screening. We discovered that PTPN12 inactivation drives mitotic defects through aberrant hyperactivation of the ubiquitin ligase complex APCFZR1, a critical regulator of the cell cycle. Consistent with the mitotic stress caused by PTPN12 inactivation in TNBC cell lines, tumors harboring loss of PTPN12 exhibit heightened sensitivity to taxane chemotherapy. Collectively, these data suggests that PTPN12 inactivation may drive chromosomal instability and favorable MTA response in TNBC—two prominent features of the disease with unclear mechanistic etiology.
AJRCCM [IF=19.4]

文獻引用產品:
摘要:
Rationale: Early-life lung function trajectories predict long-term respiratory health, including COPD risk. Club Cell protein 16 (CC16) is a key determinant of lung health, with low levels associated with impaired lung development, reduced lung function, and COPD. Cigarette smoking lowers CC16, but it is unknown whether maternal smoking leads to persistent CC16 deficiency from early life, thereby disrupting lung development and predisposing to COPD risk and progression.
Methods: CC16 expression was analyzed across 4 human cohorts, in plasma samples (COPDGene [n=1,062] and ECLIPSE [n=2,164]), nasal brushings (ALLIANCE [n=63]), and peripheral lung sections (LTRC [n=44]) from participants with and without a history of maternal smoking exposure. Lung histology and respiratory mechanics were assessed in WT and Cc16-/- mice with and without maternal smoking exposure. Recombinant human (rh)CC16 effects on lung maturation were assessed in embryonic murine lung explants.
Results: Maternal smoking was linked to reduced circulating and airway CC16 in COPD patients, controls, and a preclinical murine COPD model. In human adults, lower CC16 correlated with accelerated lung function decline and emphysema progression, while in children it was associated with obstructive physiology and early small airway impairment. In both mice and humans, maternal smoking–induced CC16 reduction was accompanied by greater epithelial injury (fibrosis, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress). In murine explants, smoking impaired lung branching, whereas rhCC16 restored branching via α2- integrin binding.
Conclusions: Maternal smoking reduces CC16 levels, disrupting lung development in ways that predispose to lifelong impairment of lung function and worse COPD outcomes. Defining the mechanisms by which CC16 regulates lung maturation is essential for establishing reliable outcome measures and designing trials aimed at preventing early COPD.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文獻引用產品:
摘要:Serving as the cornea's outermost barrier, the corneal epithelium is susceptible to persistent damage, which can lead to irreversible vision loss and severe neuropathic pain. Electrical stimulation bandage contact lenses (BCLs) can provide wound protection while accelerating the healing process. However, their opacity and complex design hinder their clinical adoption. This study proposes a bioactive BCL using poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) (P(VDF-TrFE)) through a simple fabrication process, which exhibits outstanding transparency and the ability to generate a uniform microelectric field over the injury site, while also offering superior smoothness, mechanical, and electrical properties. In vivo and in vitro experiments confirmed the excellent biocompatibility and effectiveness of P(VDF-TrFE) BCLs in corneal epithelial wound healing, with RNA-sequencing revealing the underlying mechanisms associated with corneal injury healing, such as cytoskeletal reorganization and inflammation regulation. Furthermore, the reorganization of the cytoskeleton and pseudopodia, which enhances the cellular ability to sense the injury environment and to promote migration and proliferation, is validated in co-cultured human corneal epithelial cells. Additionally, P(VDF-TrFE) BCLs inhibit excessive inflammation during the injury process, promoting a favorable healing environment. These findings position P(VDF-TrFE) as a promising treatment option for corneal injuries, highlighting the broader potential of ferroelectric polymers in ophthalmic tissue engineering.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文獻引用產品:
bs-1035R | CD86 Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:西安交通大學第二附屬醫院
摘要:Intrauterine adhesions (IUA) are characterized by fibrotic repair and partial or complete occlusion of the uterine cavity, resulting from endometrial damage. The occurrence of IUA can adversely affect the reproductive and physiological health of women. Developing a delivery platform capable of loading various bioactive agents to achieve personalized treatment strategies can significantly enhance IUA therapy. In this study, cryopolymerization is employed to fabricate an antifouling porous scaffold (GNP) with shape memory properties, serving as a delivery vehicle for bioactive agents. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrate that GNP can incorporate multiple bioactive agents (penicillin-streptomycin (PS), stem cell exosomes (Ex) and N-acetylcysteine (NAC)), and promote their sustained retention. Based on the core factors of adhesion formation, the antioxidant NAC is chosen as a model agent combined with GNP. In the rat IUA model, NAC-loaded GNP (P150N) modulates the endometrial microenvironment through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic actions. P150N effectively facilitates endometrial regeneration, reduces adhesion formation, and significantly increases embryo implantation rates. Additionally, proteomics analysis reveals that the P150N significantly downregulates proteins associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, while upregulating those involved in cell proliferation. Overall, this work presents a versatile platform, offering a potential personalized therapeutic strategy for IUA prevention.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文獻引用產品:
作者單位:四川大學
摘要:As a major causative agent of cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis (AS) is typically characterized by aberrant lipid buildup and persistent vascular inflammation. However, early AS is difficult to recognize by traditional imaging methods owing to the absence of evident symptoms. Therefore, a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive theranostic nanoplatform (PA/HFLCD) is developed in order to modulate the endothelial cell-macrophage crosstalk in a pathological environment and to enable precise detection of early plaques. π-conjugated polymers (PFDPP-Se) are synthesized by palladium-catalyzed arylation polymerization reaction. β-Cyclodextrin-modified oxidized dextran is self-assembled with ferrocene and linoleic acid co-modified low molecular weight heparin, incorporating PFDPP-Se as photoacoustic contrast agents. Excessive ROS at the plaque facilitates the breakdown of ferrocene binding to β-cyclodextrins, releasing both PFDPP-Se and therapeutic agents to identify lesions by photoacoustic imaging and balancing endothelial cell-macrophage crosstalk. In vivo studies confirm that PA/HFLCD enables precisely targeted photoacoustic diagnostics and regulates the inflammatory microenvironment consisting of endothelial cells and macrophages in ApoE?/? mice, leading to plaque regression. This synergistic amalgamation of diagnostic and therapeutic attributes renders PA/HFLCD not only a formidable instrument in combating AS, but also a reference for the theranostics of various inflammatory diseases.
ACS Nano[IF=16]

文獻引用產品:
作者單位:廣州醫科大學附屬醫院
ACS Nano[IF=16]

文獻引用產品:
bsm-33004M | His tag Mouse mAb | WB
bs-0296G-HRP | Goat Anti-Mouse IgG H&L, HRP conjugated | WB
bs-13151R | FCGRT Rabbit pAb | FC
SV2000 | 單克隆抗體制備 | FC
作者單位:蘭州大學